Maple Syrup Urine Disease (MSUD) Animal Model Service
In vivo studies for maple syrup urine disease (MSUD) are essential as they provide a complete physiological context to evaluate disease mechanisms and therapeutic efficacy, which cannot be fully replicated in vitro. Protheragen is committed to providing comprehensive animal models for MSUD to advance in vivo research, enabling critical investigation into disease mechanisms and therapeutic development.
Introduction to Maple Syrup Urine Disease (MSUD) Animal Models
Maple syrup urine disease (MSUD) animal models are specialized preclinical tools that accurately replicate the disease's core metabolic and neurological characteristics. These models consistently demonstrate the hallmark biochemical abnormalities of MSUD, including elevated branched-chain amino acids and their corresponding keto-acids. Their primary value lies in enabling critical research into disease mechanisms and providing reliable platforms for evaluating new treatment approaches, from dietary interventions to advanced gene therapies.
 Fig.1 Muscle-directed AAV gene therapy rescues the maple syrup urine disease phenotype in a mouse model. (Jenny A. Greig, et al., 2021)
Fig.1 Muscle-directed AAV gene therapy rescues the maple syrup urine disease phenotype in a mouse model. (Jenny A. Greig, et al., 2021)
Our Services
Leveraging advanced technology and a dedicated team, Protheragen offers comprehensive animal model development services for maple syrup urine disease (MSUD) research, supporting the advancement of therapeutic strategies for this complex neurometabolic disease. Our highly validated models recapitulate key neuropathological and behavioral phenotypes, making them indispensable tools for studying disease mechanisms, validating targets, and testing the efficacy of novel drugs or therapies.
Animal Models of Maple Syrup Urine Disease (MSUD)

Protheragen specializes in developing highly reliable genetically engineered models for maple syrup urine disease (MSUD), with particular expertise in advanced knockout (KO) technologies.
- Bckdha Knockout Mouse Model
- Bckdhb Knockout Mouse Model
- Dbt Knockout Mouse Model
- More
Featured Animal Models
| Model Name | Modeling Method | Sales Status | Detailed Description |
| Dbt-KO Mice | Knockout | Sperm Cryopreservation | Exon 2 of Dbt gene was deleted to generate Dbt knockout mice. |
| Ppm1k-KO Mice | Knockout | Embryo Cryopreservation | Exon 3 of Ppm1k gene was deleted to generate Ppm1k knockout mice. |
| Prf1-KO Mice | Knockout | Embryo Cryopreservation | This Prf1 knockout mouse model was generated by knocking out the exon 3 region of the Prf1. |
Case Study-Bckdha−/− Mouse Model
Model Introduction
This case study details the generation and molecular characterization of the Bckdha−/− mouse model for maple syrup urine disease (MSUD). MSUD is an inherited metabolic disorder caused by defects in the branched-chain α-ketoacid dehydrogenase (BCKD) complex, leading to the accumulation of branched-chain amino acids. The BCKDHA gene encodes the E1α subunit, which is essential for the complex's catalytic function. Our model aims to recapitulate the core molecular deficiency of this severe condition.
Methodology
- Animal Model: Bckdha−/− homozygous knockout mice on a C57BL/6N background and Bckdha+/+ wild-type controls.
- Modeling Method: Our scientists generate the Bckdha−/− mouse model for MSUD research through targeted gene editing-mediated knockout of the Bckdha gene or via breeding strategies using existing heterozygous mutants.
- Molecular Analysis Methods:
- Gene Expression Analysis: Bckdha mRNA levels were quantified by RT-PCR in liver, heart, and brain tissues.
- Protein Expression Analysis: BCKDHA protein levels were assessed by Western blot in the same tissues to confirm the knockout at the protein level.
Phenotypic Analysis & Results
Molecular analysis confirmed the successful generation of a complete knockout model at both transcriptional and translational levels.
- Absence of Bckdha Transcripts: RT-PCR analysis demonstrated that Bckdha mRNA was nearly undetectable in the liver, heart, and brain of Bckdha−/− mice compared to Bckdha+/+ mice (Fig.2A).
- Complete Loss of BCKDHA Protein: Western blot showed similar results for BCKDHA protein in the liver, heart, and brain, confirming the null nature of the Bckdha−/− mouse model (Fig.2B).
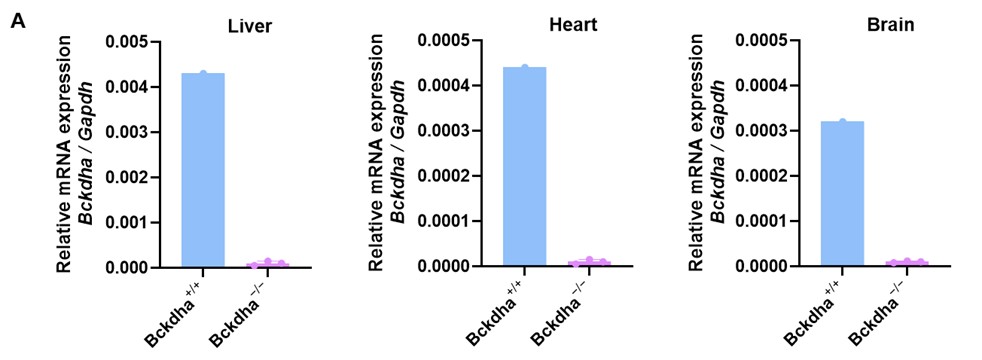
 Fig.2 Molecular validation of the Bckdha−/− MSUD model. (A) Bckdha mRNA expression. (B) BCKDHA protein expression. All data are shown as means ± SD. (1 week, Bckdha−/− n = 3, Bckdha+/+ n = 1).
Fig.2 Molecular validation of the Bckdha−/− MSUD model. (A) Bckdha mRNA expression. (B) BCKDHA protein expression. All data are shown as means ± SD. (1 week, Bckdha−/− n = 3, Bckdha+/+ n = 1).
Conclusion
This case study confirms that the Bckdha−/− mouse is a precise molecular model for studying maple syrup urine disease (MSUD). The model demonstrates the near-complete absence of Bckdha mRNA and BCKDHA protein in key metabolic tissues, confirming it as a true null model. This model provides an important platform for studying the pathogenesis of MSUD, evaluating novel therapeutic interventions, and advancing biochemical research on the function and regulation of the BCKD complex.
Contact Us
Specializing in preclinical drug development solutions, Protheragen offers comprehensive animal models to advance pharmacodynamics (PD), pharmacokinetics (PK), and toxicology studies, thereby supporting the development and regulatory approval of potential therapies. If you are interested in our animal model development services, please do not hesitate to contact us for more details and quotation information.
Reference
- Jenny A. Greig, et al. Muscle-directed AAV gene therapy rescues the maple syrup urine disease phenotype in a mouse model[J]. Molecular Genetics and Metabolism, 2021, 134(1-2): 139-146.




